Inside Sanas Voice Activity Detection (VAD) for Real-Time, Low-Latency Applications

Voice Activity Detection (VAD) is a foundational component of modern speech technology systems. Whether it’s powering keyword spotting, Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) transcription systems, or real-time speech processing models, VAD determines when speech is present — and just as importantly, when it’s not.
A strong VAD is mission critical to voice-centric applications in three ways:
- Turn Detection and Conversational Flow: For Interactive Voice Response (IVR) and voice AI agents that converse with users, a VAD helps determine when someone has stopped speaking — a core part of “turn detection”.
- Avoiding Spurious Interruptions: A robust VAD ensures that AI systems don’t react to background voices or random noise. This avoids unnecessary interruptions, false triggers of downstream models, or unintended responses, keeping conversations continuous and natural.
- Efficiency and Cost Savings: Because VAD filters out non-speech frames, systems don’t waste resources processing silence or background noise. This leads to lower compute and bandwidth usage, which are important in cloud-based ASR, LLM pipelines, or mobile voice-app scenarios.
Even though real-time VAD systems have been around for years, most weren’t built for the environments we’re dealing with today. They work well in clean or controlled settings, but once you introduce real-world noise — overlapping voices in a call center, a fan blowing into the microphone, someone talking from across the room — their accuracy quickly decreases. Unfortunately, those are exactly the scenarios where modern voice-AI systems need VAD to be rock solid.
The limitations of existing real-time VAD make one thing clear: modern speech systems need a VAD built for streaming, real-world acoustics, and strict latency requirements.
That’s why we built Sanas Voice Activity Detection (VAD), our latest generation system designed specifically for real-time, low-latency streaming applications and challenging acoustic environments. With Sanas VAD, conversations become clearer, downstream models are more efficient, and speech-driven systems respond with greater precision.
In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into core innovations that make Sanas VAD different, its verified results against leading VAD models, and what its performance means for modern voice-AI systems.
Introducing Sanas VAD: A Leap Forward in Streaming Speech Intelligence
Instead of trying to patch the weaknesses of traditional VAD approaches, we rethought the problem from the ground up specifically for the realities of streaming speech: low latency, unstable acoustics, and rapid turn-taking. Across our research and customer deployments, we identified three core areas where a next-generation VAD could make the greatest impact.
Precision in the Real World: Sanas VAD delivers higher detection accuracy compared to leading models across a wide range of acoustic conditions — from busy streets and open offices to far-field microphones and environments with multiple overlapping speakers.
Built with advanced neural front-end processing and adaptive temporal modeling, it reliably distinguishes speech from background noise. This level of robustness isn’t just a performance boost; it’s what allows downstream systems to behave predictably in the real world.
Streaming-Native by Design: Most VAD systems work well offline where they can leverage the entire audio context and apply heavy post-processing, analyzing future frames to refine its predictions. This accuracy comes with a cost: it increases latency by several hundred milliseconds.
Real-time applications don't have that luxury. In streaming applications, VAD must make immediate, confident decisions with minimal context and near-zero latency.
Sanas VAD was engineered specifically for this constraint. We tackled this challenge with a streaming-optimized architecture that maintains high accuracy while using just 40ms of lookahead, enabling near-instant detection and smooth conversational flow. It also produces predictions at 100 Hz. This means it updates its speech/non-speech decision every 10 milliseconds, which allows it to detect the beginning and end of speech with extremely fine temporal resolution.
This design makes it ideal for turn-taking, live conversation agents, and low-latency pipelines that need to react instantly, capturing even very short speech bursts — crucial for natural conversational flow.
- Lightweight, Scalable, and Efficient: Through careful design and efficient convolutional–recurrent encoding, Sanas VAD delivers high accuracy while maintaining a compact footprint suitable for real-time edge deployment in resource-constrained environments.
Together, these three architectural choices give Sanas VAD the accuracy, stability, and responsiveness required in real conversational environments. To support the many ways voice systems operate in practice — from shared microphones to single-speaker interactions — Sanas VAD also includes flexible operating modes.
Two Smart Modes for Real-World Use: Standard and Voice Isolation Mode
Sanas VAD supports two operating modes that reflect how speech systems are used in practice — across both human and AI agent use cases — whether the goal is to capture every speaker in a shared environment or isolate the primary talker when clarity matters most.
- Standard Mode: Detects all speakers’ voices and ignores noise, making it perfect for group calls or shared-microphone environments.
- Voice Isolation Mode: Focuses solely on the foreground speaker, effectively filtering out other background speech before the signal reaches downstream models.
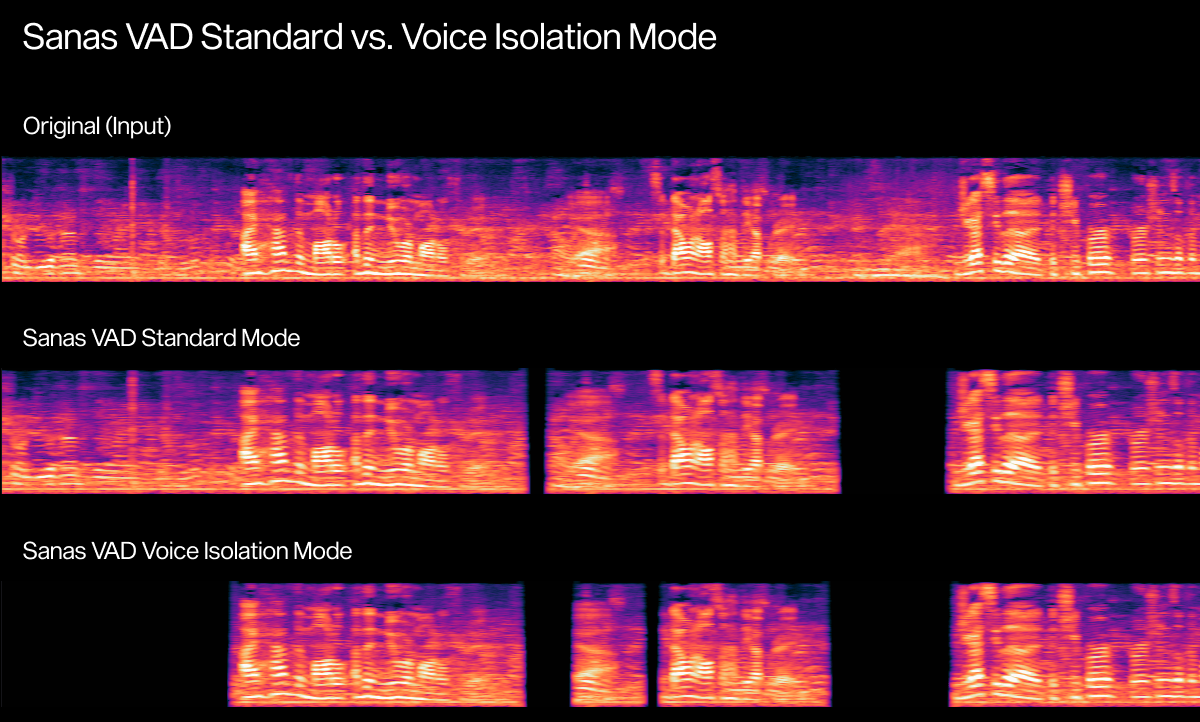
Original (Input) | Sanas VAD Standard Mode | Sanas VAD Voice Isolation Mode |
By offering both multi-speaker and foreground-focused operation, Sanas VAD accommodates the varied acoustic and interaction patterns seen in human and AI agent workflows alike.
Built for the Future: Scientifically Validated, Real-World Proven
Sanas VAD has been evaluated across a wide set of open-source public datasets as well as in-house real-world environments including close-talk microphones, far-field recordings, multilingual speakers, overlapping voices, and a variety of noise sources.
Across these conditions, Sanas VAD demonstrates consistently strong performance. While Silero v6 remains one of the strongest open-source VAD baselines, Sanas VAD achieves higher accuracy and ROC-AUC scores on multiple benchmarks. These gains are particularly pronounced on our in-house noisy and overlapping datasets, where real conversational complexity is highest and where traditional VAD systems tend to break down.
To make this evaluation clear and accessible, we report two key metrics:
- ROC-AUC (Receiver Operating Characteristic — Area Under Curve): A measure of how well a model separates speech from non-speech across all thresholds. Higher values indicate a stronger ability to distinguish the two without being overly sensitive to noise or silence.
- Accuracy: The proportion of correct predictions the VAD makes relative to the total number of predictions. Correct predictions include True Positives (TP, correctly predicted positives) and True Negatives (TN, correctly predicted negatives), and incorrect predictions include False Positives (FP, negatives incorrectly predicted as positives) and False Negatives (FN, positives incorrectly predicted as negatives). Accuracy helps illustrate how the model behaves at a fixed operating threshold in real scenarios.
These metrics together provide a balanced view of how reliably a VAD model performs in real-time applications.
ROC-AUC
Model | Webtrc | TenVad | Silero v6 | Sanas VAD |
AliMeeting test | 0.82 | 0.91 | 0.96 | 0.97 |
Earnings 21 | 0.86 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.97 |
MSDWild | 0.62 | 0.77 | 0.79 | 0.88 |
AISHELL-4 test | 0.74 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.94 |
VoxConverse test | 0.65 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.92 |
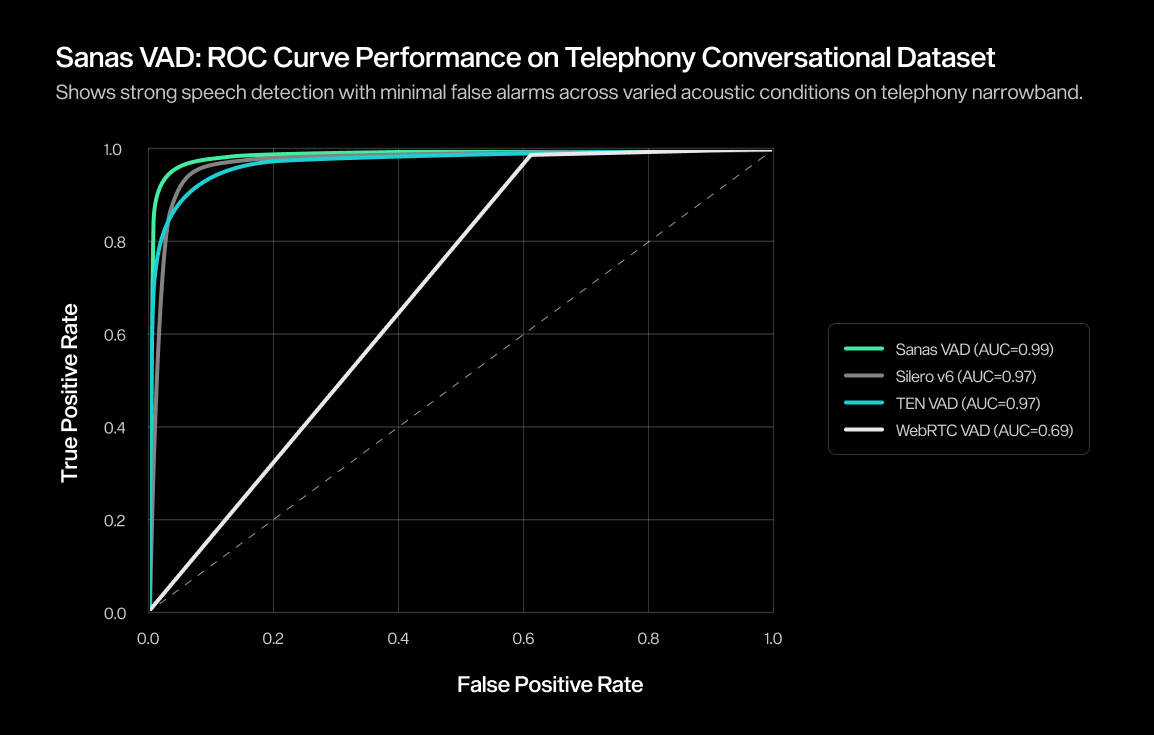
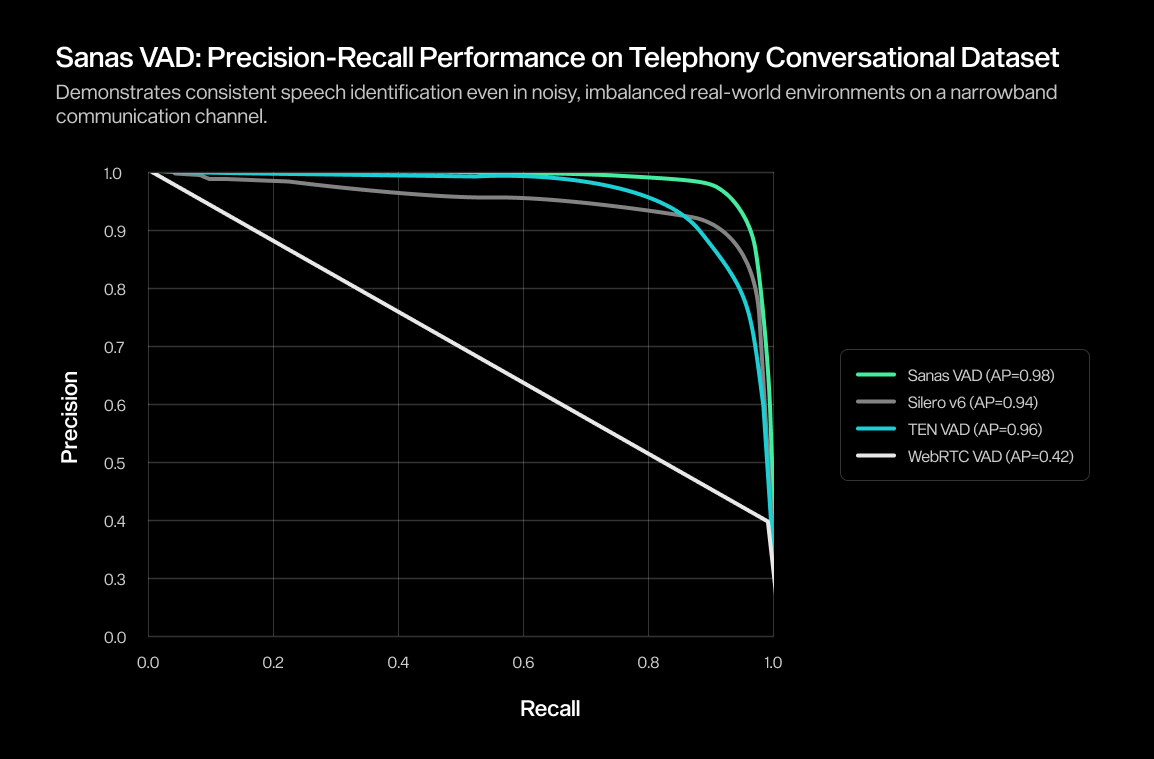
In-House Real-World Telephony Conversational Speech (8kHz) | 0.69 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.99 |
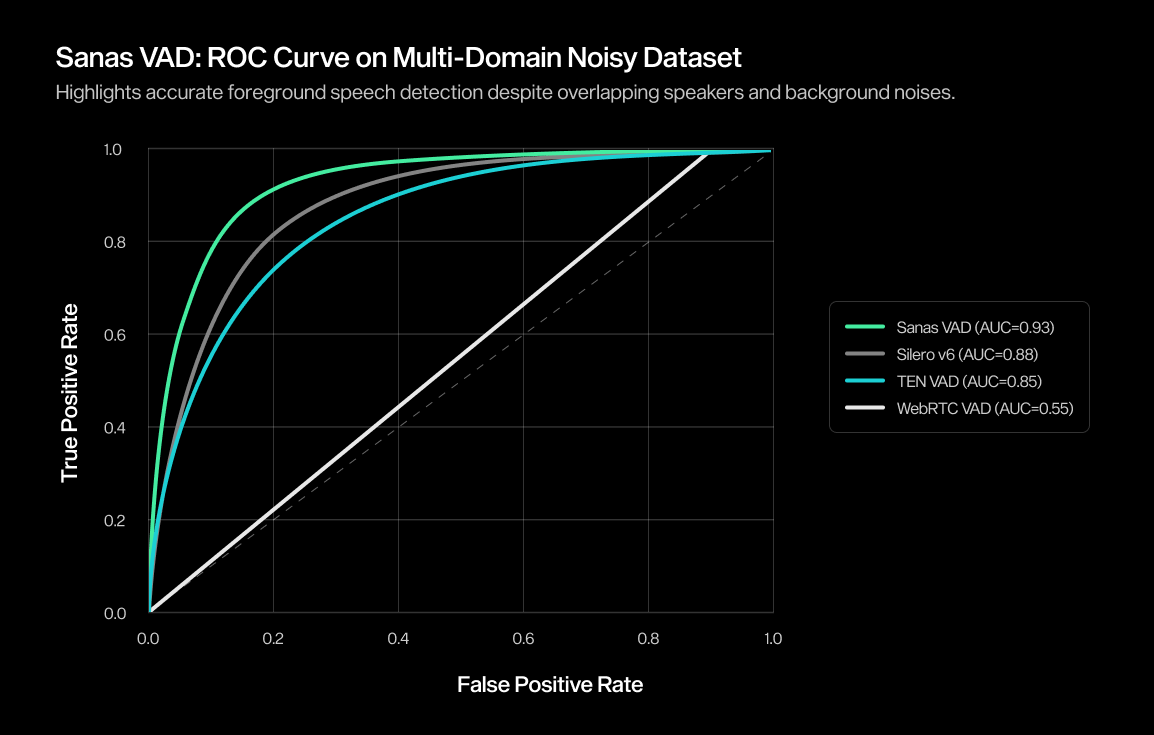
In-House Real-World Multi-Domain Noisy Speech (16kHz) | 0.55 | 0.85 | 0.88 | 0.93 |
Results are also reported in Silero’s official repository.
Accuracy
Model | Webrtc | TenVad | Silero v6 | Sanas VAD |
AliMeeting test | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.91 | 0.92 |
Earnings 21 | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.92 | 0.94 |
MSDWild | 0.83 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.86 |
AISHELL-4 test | 0.57 | 0.75 | 0.85 | 0.91 |
VoxConverse test | 0.84 | 0.90 | 0.93 | 0.92 |
In-House Real-World Telephony Conversational Speech (8kHz) | 0.58 | 0.93 | 0.85 | 0.96 |
In-House Real-World Multi-Domain Noisy Speech (16kHz) | 0.67 | 0.73 | 0.78 | 0.86 |
Results are also reported in Silero’s official repository
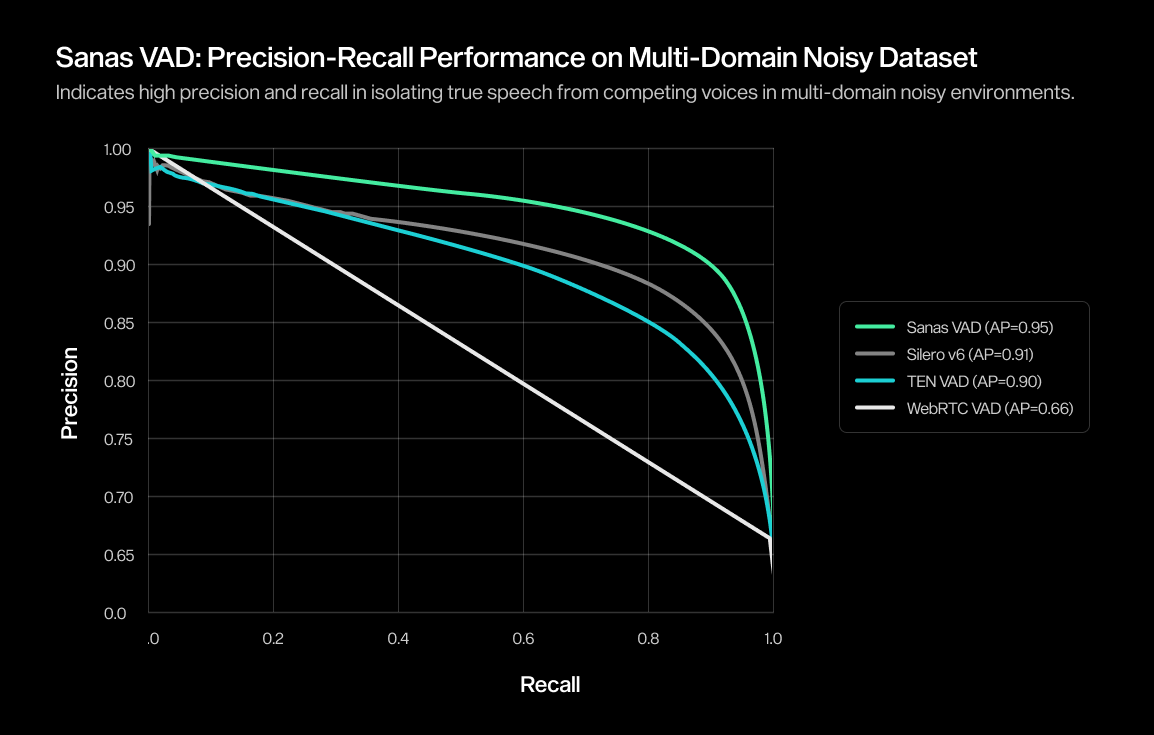
To complement the tables, we also include ROC curves and precision–recall (PR) curves on in-house real-world challenging datasets. These visualizations help illustrate how Sanas VAD performs across a wide range of thresholds — not just at a single operating point — offering a more nuanced view of robustness.
- An ROC curve shows how a VAD performs by plotting the True Positive Rate (correctly detecting speech) and the False Positive Rate (incorrectly tagging non-speech as speech). A curve that bends sharply toward the top-left corner indicates a model that can catch more real speech while making fewer mistakes.
- A precision-recall (PR) curve focuses on how well the VAD distinguishes speech from silence by plotting precision (the proportion of detected speech that is actually speech) against recall (the proportion of actual speech correctly detected) High precision means that detected speech is usually correct; high recall means the model successfully captures most spoken segments. Strong curves indicate reliability even when speech is sparse or noise is dominant.
Together, these charts show how Sanas VAD retains stable, high-confidence performance across noisy, speech-overlapping environments; conditions where many other VAD systems tend to be less consistent.
Hear Sanas VAD in Action
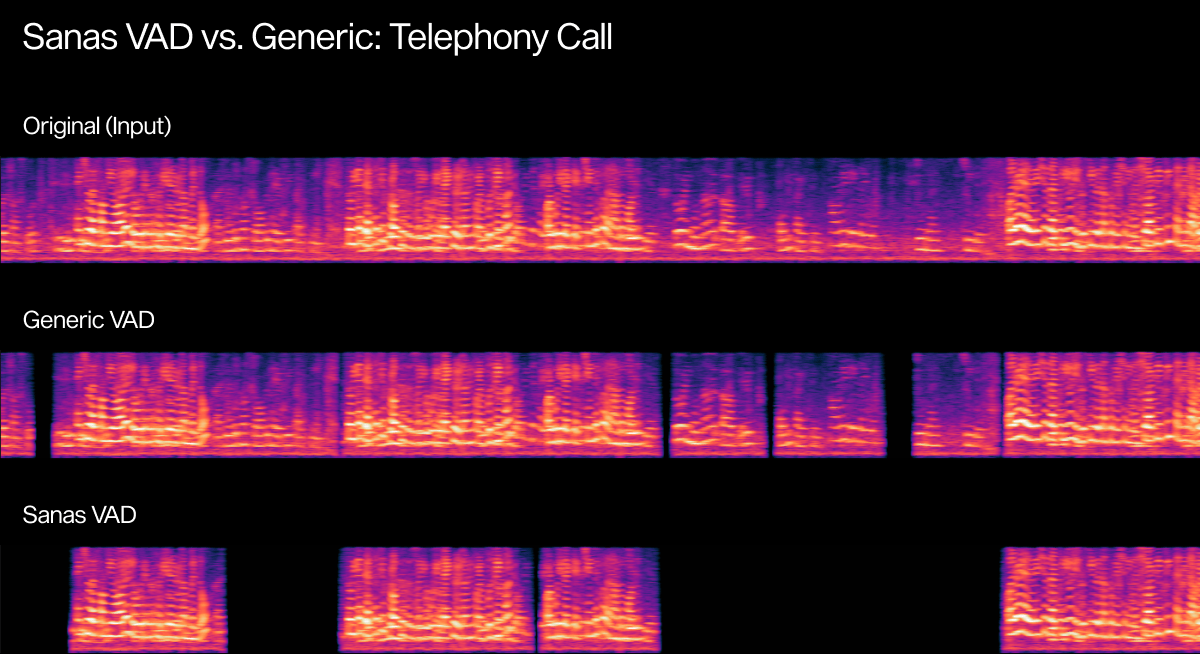
Real-world audio makes the differences clearer than any metric. Below are examples showing how Sanas VAD performs in noisy, unpredictable environments compared to a commercially available VAD system. Each scenario highlights common challenges (background chatter, overlapping voices, and/or short interjections) and how accurately each VAD model handles speech boundaries.
For each example, you’ll see:
- Original Input: Raw audio with real environmental noise
- Generic VAD: Commonly used VAD which may be prone to false activations or missed speech
- Sanas VAD: Clean speech detection with no false positives or negatives
Original (Input) | Generic VAD | Sanas VAD |
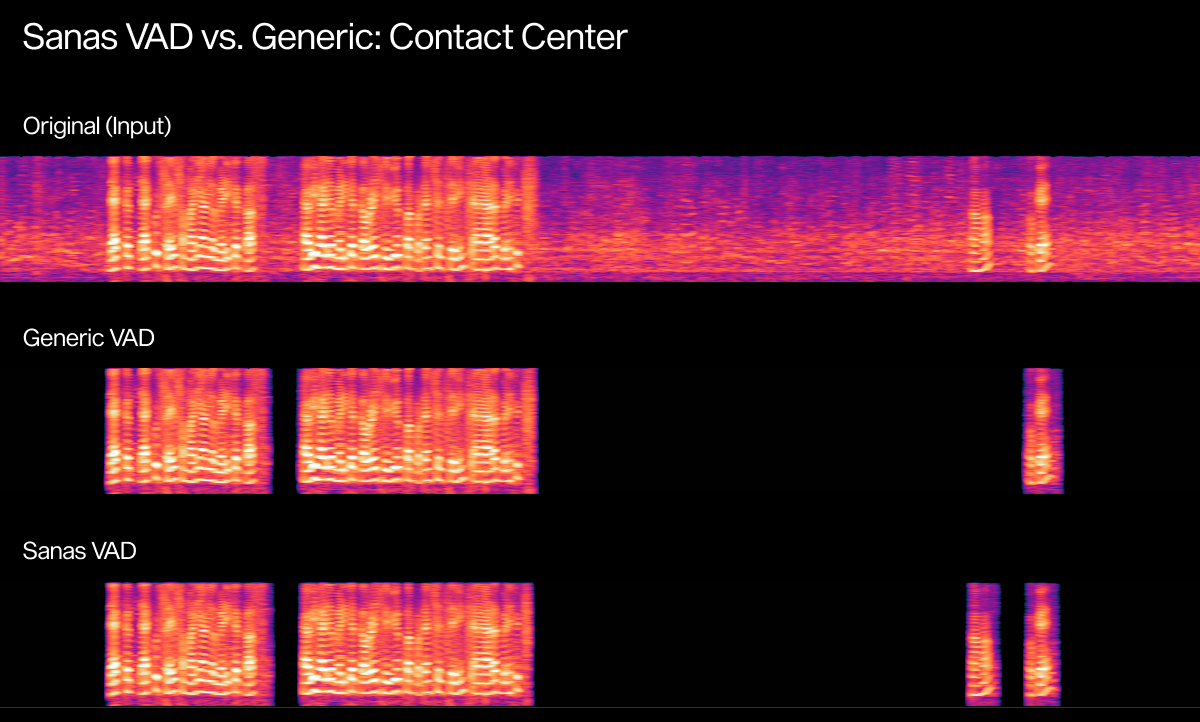
Original (Input) | Generic VAD | Sanas VAD |
The Foundation for the Next Generation of Speech Intelligence
Sanas VAD is more than a high-accuracy model, it’s a foundation for smarter, more reliable speech-driven technology.
- For developers a drop-in enhancement for Sanas SDK improves responsiveness for LLMs, language translation, and other speech-driven pipelines.
- For agentic AI: sharper turn-taking and background noise suppression enhances dialogue fluidity and system awareness.
- For enterprise integrations: reduces compute load and boosts downstream model reliability by delivering cleaner, context-ready speech segments.
Sanas VAD represents a milestone in our mission to build inclusive, reliable, real-time speech intelligence, which depends on understanding when someone is speaking, how they’re speaking, and what signals actually reflect human intent. Sanas VAD brings that clarity to environments where legacy VAD struggles most: noisy, multilingual, fast-moving conversations that define today’s global communication.
With its combination of accuracy, efficiency, and ultra-low-latency design, Sanas VAD marks a meaningful step toward helping machines understand humans better. This is just the beginning, as we set the groundwork for the next generation of AI systems that can listen more carefully, respond more naturally, and connect people more clearly no matter the environment.












